Fabric Weight: A Guide to Choosing Woven Fabrics
🧵 Understanding Fabric Weight in Fashion Design
Fabric weight plays a crucial role in garment design and manufacturing. It affects not only the drape, structure, and silhouette of a garment, but also its cost, function, and seasonal suitability. Choosing the right weight of woven fabric ensures that a design performs as expected in both aesthetics and wearability.
📏 What Is Fabric Weight?
Fabric weight is the measurement of how heavy a fabric is per unit area. It is usually expressed in:
- Grams per square meter (g/m²) — common in Europe and Asia.
- Ounces per square yard (oz/yd²) — common in the United States.
For example:
- A lightweight fabric might weigh 100 g/m².
- A midweight fabric could be 200–300 g/m².
- A heavyweight fabric might exceed 400 g/m².


💡 Why Fabric Weight Matters
| Factor | Influence of Fabric Weight |
|---|---|
| Drape and Fit | Lighter fabrics flow; heavier fabrics hold shape |
| Volume and Structure | Heavy fabrics create more volume |
| Insulation | Heavier fabrics retain more warmth |
| Garment Type | Trousers: heavy; Shirts: light; Skirts: both |
| Production Cost | More weight = more fibers = higher cost |
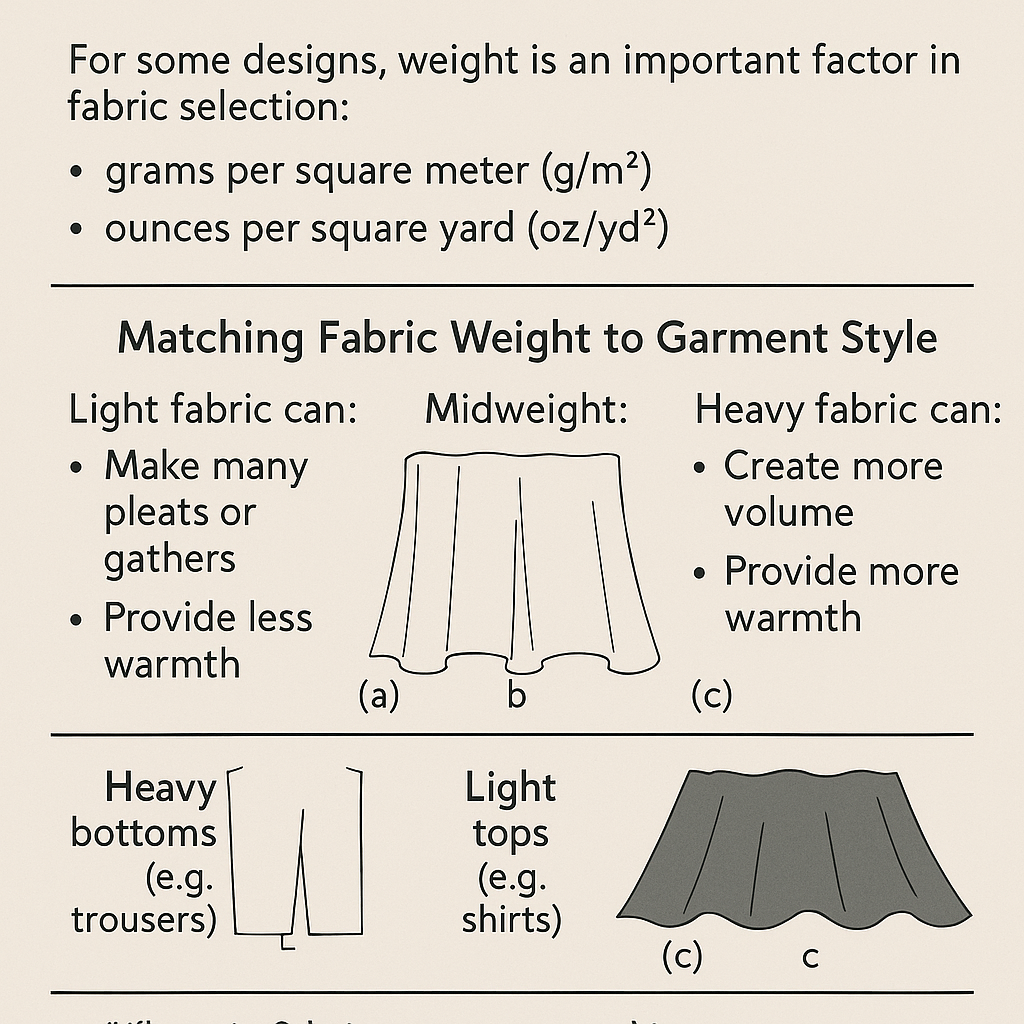
👚 Matching Fabric Weight to Garment Style
- Lightweight fabrics (e.g., voile, chiffon, organza)
Ideal for: Blouses, dresses, gathered or pleated designs
Properties: Soft drape, breathable, delicate look - Midweight fabrics (e.g., poplin, twill)
Ideal for: Shirts, skirts, casual pants
Properties: Balanced structure and drape - Heavyweight fabrics (e.g., denim, wool, corduroy)
Ideal for: Coats, trousers, suits
Properties: Structured, durable, warmer
🧵 Special Fabric Weights: The Case of Silk Satin
Silk fabrics, especially silk satin, are measured in momme (mm). A higher momme indicates:
- Denser weave
- Heavier yarns
- More luxurious drape and opacity
Examples:
- 8–12 momme: lightweight silk (scarves, lining)
- 16–19 momme: standard for dresses and blouses
- 22+ momme: high-end luxury garments
🌍 Global Considerations in Fabric Weight
Different countries and factories use varying standards:
- Always clarify whether the weight is oz/yd² or g/m²
- Double-check conversions when sourcing globally
🧷 Pro Tip for Designers
Always test drape, transparency, and weight with swatches before mass production. The right fabric weight can elevate a basic design to a standout piece—or ruin a great pattern if poorly matched.
📌 Summary Table of Common Fabric Weights
| Fabric Type | Typical Weight | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Voile | ~60–100 g/m² | Summer blouse |
| Poplin | ~120–150 g/m² | Casual shirt |
| Denim | ~300–450 g/m² | Jeans |
| Suit Wool | ~200–350 g/m² | Business suits |
| Silk Satin | 8–30 momme | Dresses, blouses, gowns |