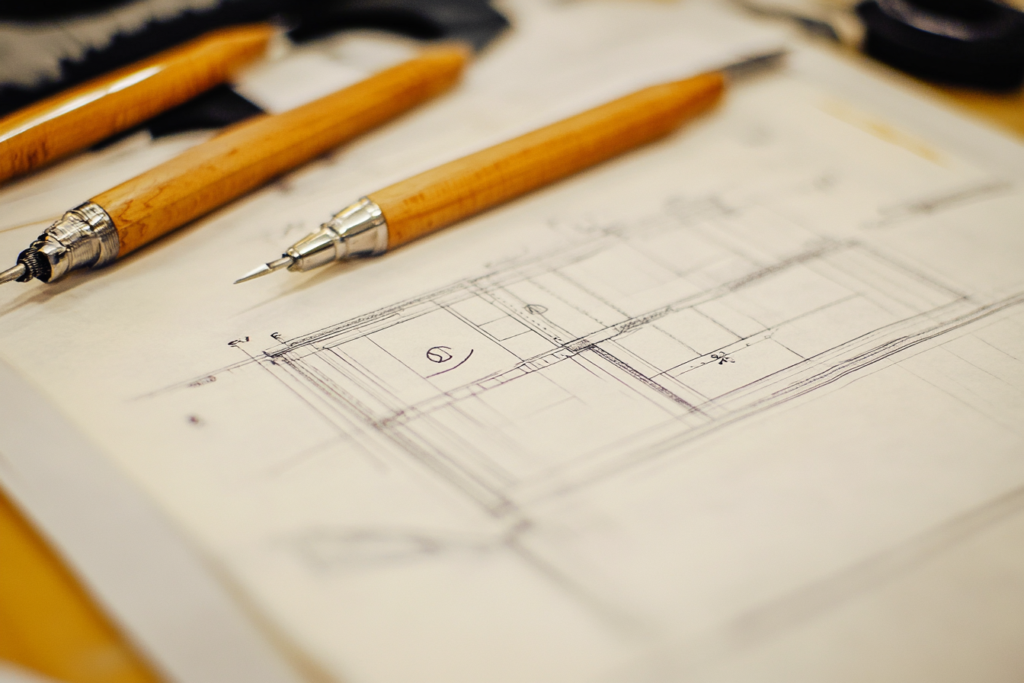
the Art of Clothing Design & Development
The foundation of any successful fashion brand lies in its ability to seamlessly translate creative ideas into market-ready garments. The clothing design and development process is a dynamic, multi-stage journey that begins with concept creation and extends through production, quality control, and market delivery. For women’s apparel, where trends shift rapidly and target markets are diverse, mastering this process is critical. In today’s fast-paced market, new collections are often released multiple times a year to keep the shelves updated with fresh styles. Designers frequently juggle multiple seasons simultaneously—working on the current collection while brainstorming ideas for the next. This multitasking and forward-thinking approach is key to meeting customer expectations and sustaining brand relevance.
Key Components of the Clothing Design & Development Process
🔑 Concept & Trend Research
Before sketching the first design, successful brands invest time in understanding current trends and consumer needs. Market research, competitor analysis, and trend forecasting help shape the creative vision.
🔑 Design & Prototyping
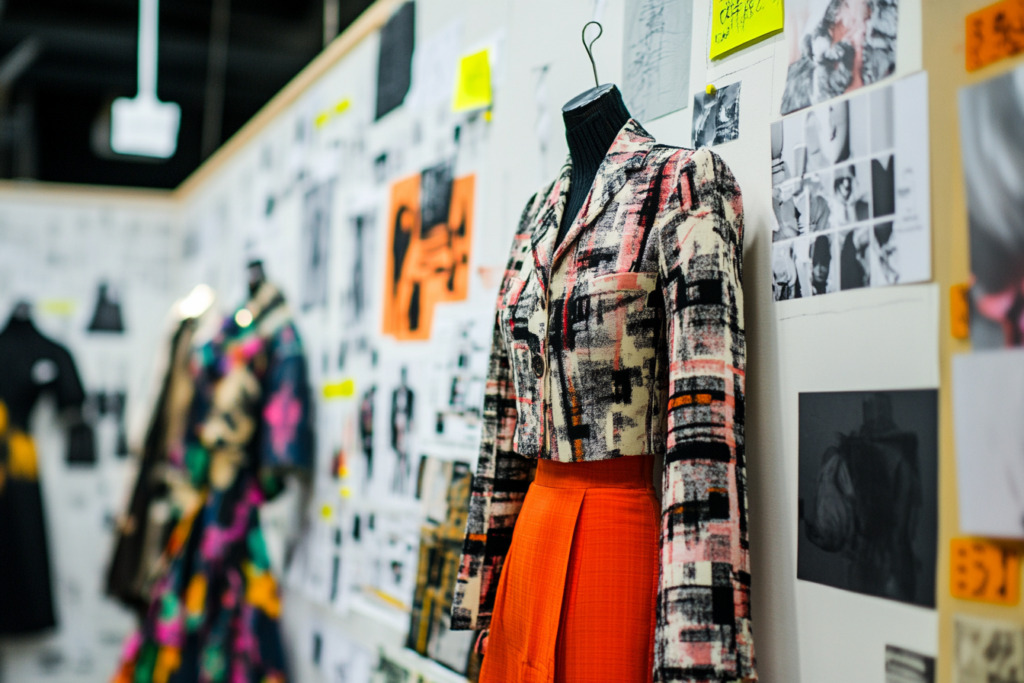
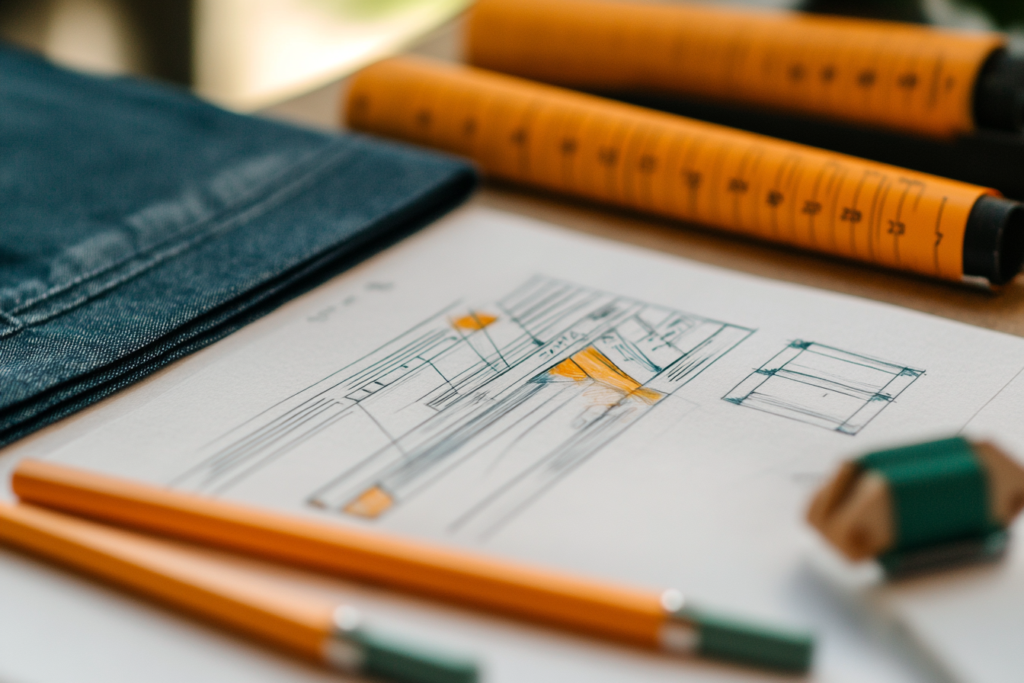
Once the concept is established, designers create technical sketches and prototypes. This phase involves selecting fabrics, refining details, and ensuring that every garment meets both aesthetic and functional requirements.
🔑 Multi-Season Planning
Women’s apparel is often divided into four to six seasonal collections. To maintain a continuous flow of new products, designers work on upcoming seasons while finalizing current ones.
🔑 Quality Control & Feedback
Rigorous quality checks ensure that prototypes meet design specifications. Customer feedback and sales data guide adjustments in sizing, fabric choice, and overall fit.
🔑 Market Launch & Branding
A well-executed launch, coupled with a consistent brand image, helps build customer loyalty. This includes aligning product pricing with quality and market positioning.
Target Market Analysis: Understanding Your Customer
For any fashion brand, knowing your target market is essential. By analyzing customer data and purchase history, brands can tailor their collections to meet specific needs. Consider the following factors:
| Factor | Importance | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Age & Gender | Determines style, fit, and fabric choice. | Teenagers may prefer trendy, casual styles, while mature women might opt for classic silhouettes. |
| Size Range | Different body types require distinct design approaches. | Designing for petite, regular, or plus sizes requires varied pattern adjustments. |
| Lifestyle | Influences the functionality and style of garments. | Active lifestyles demand athleisure, while corporate roles need professional attire. |
| Cultural Preferences | Shapes garment style and design details. | Regional influences, such as Indian kurtis or Japanese kimonos, cater to local tastes. |
Pricing Strategy and Brand Positioning
Each brand must position its products within a defined price range to match its target customers’ expectations. High-end brands emphasize luxury and exclusivity, while mass-market brands focus on affordability and broad appeal.
✅ Key Pricing Considerations:
-
- Cost-Quality Alignment: Ensure that the quality of materials and craftsmanship justifies the price.
-
- Competitive Analysis: Understand how your price point compares with similar brands in the market.
-
- Market Trends: Adjust pricing strategies based on current consumer demand and economic conditions.
-
- Brand Image: Maintain consistency between your product pricing and your overall brand positioning.
The Role of Lifestyle in Clothing Design
Clothing is not just about style—it’s a reflection of the wearer’s lifestyle and aspirations. A brand’s design philosophy should align with the lifestyles of its target audience.
🔹 Casual & Active Lifestyles:
Designs should focus on comfort and ease of movement. For example, athleisure and casual wear are designed with breathable fabrics and flexible cuts, perfect for those with dynamic, on-the-go lifestyles.
🔹 Professional & Formal Lifestyles:
Tailored garments such as structured blazers, pencil skirts, and refined dresses offer a polished look for work and formal occasions. These designs emphasize clean lines and quality fabrics.
🔹 Trendy & Fashion-Forward Lifestyles:
For younger, trend-conscious consumers, staying ahead of fashion trends is key. This might involve experimenting with bold prints, innovative cuts, or vibrant colors that capture current trends.
Key Stage of the design and development Process
Below is a simple table summarizing the key stages of the design and development process:
| Stage | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Concept & Research | Market and trend research to shape the creative vision. | 🔍 |
| Design & Prototyping | Sketching, fabric selection, and sample creation. | ✏️ |
| Quality Control | Testing prototypes, gathering feedback, and refining designs. | ✅ |
| Production & Launch | Mass production, marketing, and product launch. | 🚀 |