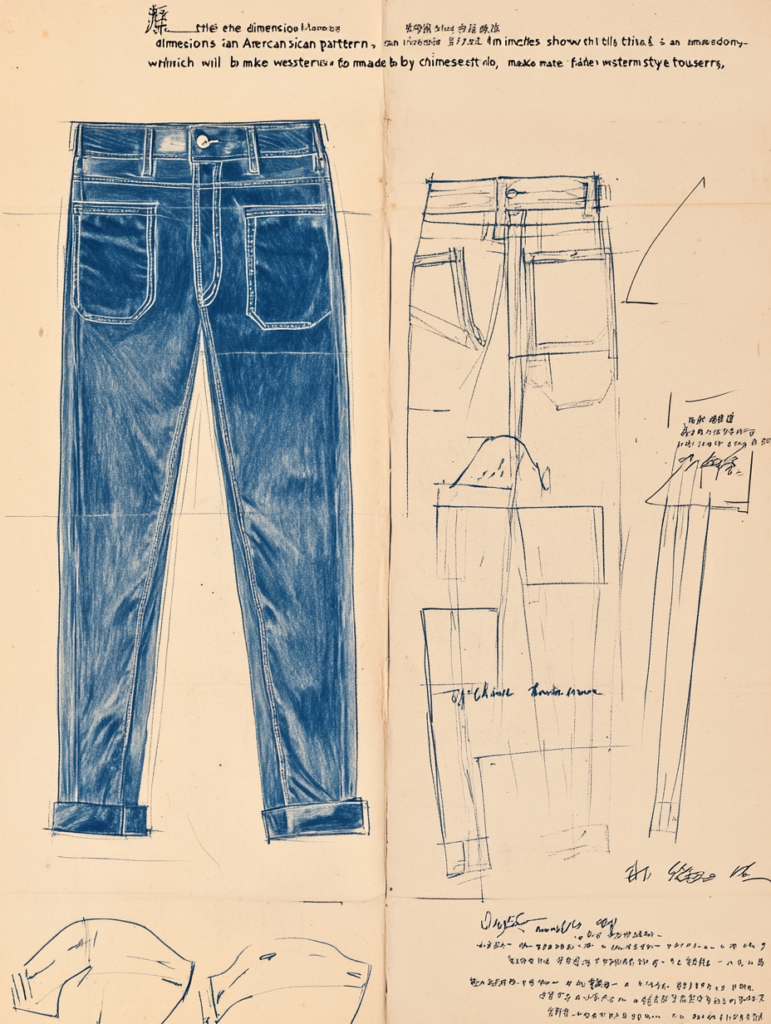
Details: A Critical Section of the Process Sheet for Garment Production
The “Details” section of the process sheet is one of the most important elements for ensuring that a garment is manufactured exactly as envisioned. This section provides in-depth descriptions and visual representations of key design features such as buttons, zippers, stitching, embroidery, and other finishing techniques. By clearly defining these details, this section ensures that the manufacturer fully understands the designer’s intentions and can replicate the garment with the correct specifications, leading to a high-quality final product.
Purpose of the Details Section
The Details section serves as a clear and precise reference for all the small but critical elements that make up the garment’s overall aesthetic and functionality. Whether it’s the type of button used, the color of the thread for stitching, or the method of attaching zippers, this section allows the designer to convey the intricate elements that can’t be captured simply in flat sketches or measurements.
By providing clear and thorough details, this section helps:
- Prevent mistakes: The more precise the details, the less room for error in the final production.
- Ensure consistency: Ensures that each garment produced in a collection looks identical, even if multiple units are being manufactured.
- Maintain design integrity: Accurately capturing design elements allows the garment to match the intended look and feel.
Key Elements Typically Included in the Details Section
Buttons
Buttons are one of the most common garment details and are often central to the garment’s aesthetic and functionality. The Details section must specify the type, size, color, material, and placement of buttons.Key details to include:
- Type of Button: Whether it’s a regular button, snap button, or decorative button, the type needs to be specified.
- Material: Buttons can be made of various materials such as plastic, wood, metal, or fabric. The material used will affect both the look and the durability of the button.
- Size: Include the exact dimensions of the buttons (e.g., 20mm or 1 inch).
- Placement: Indicate where buttons should be placed, including buttonhole positions and spacing between buttons.
- Color: The color of the buttons should be specified to match or contrast with the fabric.
Visuals: Close-up images or illustrations of buttons should be included, showing the exact size, shape, and material to avoid any ambiguity during production.
Zippers
Zippers serve both a functional and aesthetic role in garments, and their proper inclusion in the Details section ensures that they are used correctly for both. The process sheet should specify the type, length, material, and placement of zippers.Key details to include:
- Type of Zipper: Specify whether it’s an invisible zipper, exposed zipper, two-way zipper, or decorative zipper.
- Length and Dimensions: Provide the exact length of the zipper required for the garment.
- Material: Zippers come in various materials such as plastic, metal, or coil. The material can significantly impact the garment’s durability and aesthetic.
- Placement: The process sheet should indicate whether the zipper is on the side, back, or front of the garment, and whether it’s meant to be functional or purely decorative.
- Finish Type: Specify whether the zipper needs to be finished with a special technique, such as being hidden in a seam or encased in fabric.
Visuals: Provide images or sketches that show how the zipper should appear on the garment, including any special details such as zipper pulls or finishes.
Stitching and Seams
Stitching plays a fundamental role in the construction and durability of a garment. The Details section should specify not only the type of stitching but also the specific areas where it’s applied. This ensures that the garment is durable, looks polished, and fits as intended.Key details to include:
- Type of Stitching: Specify the stitch type—whether it’s single needle, double needle, overlock, or a decorative stitch. Each stitch type serves a different purpose, from basic construction to decorative detailing.
- Thread Type and Color: Indicate the material (cotton, polyester, nylon) and the color of the thread to be used. The color should either match the garment or contrast with it, depending on the design.
- Stitch Length: Provide guidelines for stitch length to ensure consistency across the garment.
- Seam Types: Different types of seams, such as French seams, flat-felled seams, or bound seams, should be clearly specified, particularly in areas where strength and appearance are key.
- Special Stitching Effects: If the garment involves intricate stitching, such as topstitching or embroidery, this should be explicitly noted.
Visuals: Illustrations of stitch types and detailed images of seam placements can help clarify these specifications for the manufacturer.
Embroidery
Embroidery can add intricate and decorative elements to a garment. The Details section should provide all the necessary specifications for embroidery placement, design, thread type, and colors.Key details to include:
- Design: A clear and detailed description of the embroidery design (floral, geometric, logo, etc.) is essential.
- Placement: Indicate the exact location on the garment for the embroidery (e.g., center chest, sleeve, hem).
- Thread Material and Color: Specify the thread used (silk, cotton, metallic, etc.) and its exact color to ensure the final product matches the intended design.
- Size and Scale: Provide dimensions for the embroidery to ensure it is applied at the correct scale.
- Technique: If any specific embroidery techniques (e.g., satin stitch, French knots, or appliqué) are used, this should be detailed in the process sheet.
Visuals: Include high-resolution images or illustrations of the embroidery pattern and placement on the garment.
Trims and Other Decorative Features
Decorative trims, such as lace, piping, and ruffles, can make or break the garment’s look. The Details section should specify the type, size, and placement of any decorative trims.Key details to include:
- Type of Trim: Identify whether the trim is lace, piping, fringe, or other materials.
- Size and Dimensions: Clearly state the width or size of the trim.
- Material: Specify the fabric or material used for the trim (e.g., satin ribbon, velvet piping).
- Placement: Indicate where each trim should be placed (e.g., along the collar, sleeve hems, or waistline).
Visuals: Provide close-up images or swatches of the trims to ensure the correct material and design are used.
Other Finishing Techniques Other finishing details that affect the garment’s final look and feel—such as raw edges, frayed hems, or fabric bonding—should also be specified in this section.
Key details to include:
- Edge Finishing: Indicate if raw edges should be left unfinished or if they need to be bound or hemmed.
- Fraying or Distressed Effects: If the design calls for distressed or frayed areas, specify how and where this should be applied.
- Bonding or Laminating: If the garment includes bonded fabric or laminated areas, provide clear instructions on where and how to apply this effect.
Visuals: Illustrate any special finishing effects to ensure the correct execution of these details.