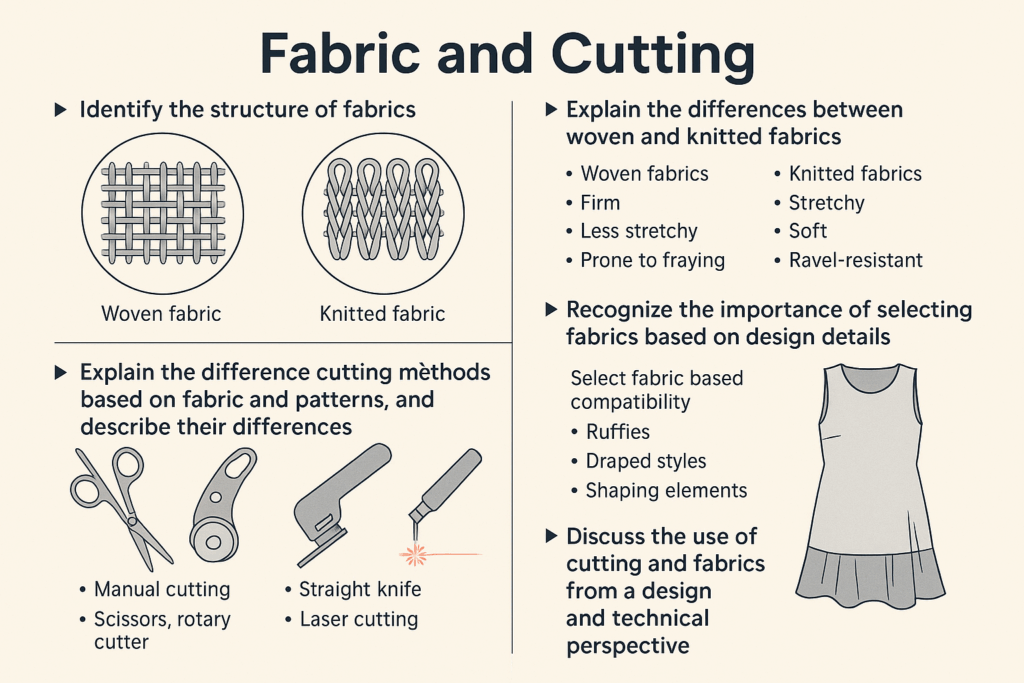
🧵 Knitted Fabrics: Structure, Types, and Applications in Fashion
Knitted fabrics are essential in modern apparel due to their flexibility, softness, and breathability. Unlike woven fabrics, knitted fabrics are created from a series of interconnected loops, providing natural stretch and comfort. These properties make them ideal for garments such as T-shirts, sportswear, children’s wear, and even evening dresses.
What Are Knitted Fabrics?
Knitted fabric is made by looping yarns through each other in a structured, interlocked pattern. The result is a material that stretches, breathes, and fits comfortably against the skin. Depending on the yarn type and knitting machine, these fabrics can vary from sheer and lightweight to thick and thermal.


Types of Knitted Fabrics
🔹 Weft Knitted Fabrics
- Constructed by running yarn horizontally.
- Produced using flat or circular knitting machines.
- Examples include jersey, rib, and double-knit fabrics.
- Commonly used for T-shirts, sweaters, and baby garments.
- Loops are interlocked row by row, creating courses (horizontal) and wales (vertical).
- Easily unravel if one stitch breaks.
🔹 Warp Knitted Fabrics
- Yarn runs vertically through the fabric.
- Created using warp knitting machines like Raschel and Tricot.
- Used in lingerie, swimwear, and sportswear.
- Stronger structure, more stable, less stretchable than weft knits.
- Doesn’t unravel easily, providing durability and firmness.
Characteristics of Knitted Fabrics
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧶 Elasticity | Naturally stretchable due to the looped yarn structure |
| ✂️ Cutting Direction | No defined bias, but still follows grain rules for cutting |
| 💧 Wrinkle Resistance | Resists creases better than woven fabrics |
| 🔍 Transparency | Typically not see-through, depending on yarn weight |
| 🔄 Curling Edge Issue | Fabric edges may curl; common in jersey and plain knits |
| 🔧 Durability | Slightly lower than woven fabrics; more susceptible to snagging |
How Knitted Fabrics Are Used in Garment Design
- Close-fitting Garments: Elastic nature allows for body-hugging but comfortable silhouettes.
- Seamless Garments: Tubular knit fabrics are often used in T-shirts to reduce labor and seams.
- Lightweight Casualwear: Ideal for warm-weather clothing and activewear.
- Evening Dresses: Fine knits like stretch jersey offer a flowy, elegant appearance.
⚠️ Note for Manufacturers: Stretch and thickness variations impact sizing. It’s crucial to pre-relax the fabric before cutting to prevent shrinkage.
Tips for Working with Knitted Fabrics
- Use ballpoint needles to avoid damaging the fabric structure.
- Stabilize shoulder seams to prevent distortion.
- Store fabric flat to avoid edge curling.
- Avoid bias cuts, as knits have inherent stretch—bias cutting doesn’t add further drape.
Summary
Knitted fabrics are a staple of contemporary fashion design due to their comfort, stretch, and versatility. Understanding the differences between weft and warp knits, and their unique properties, is essential for designers, pattern makers, and garment factories alike. Whether you’re creating a casual tee or elegant eveningwear, knit fabric offers limitless potential for creativity and function.