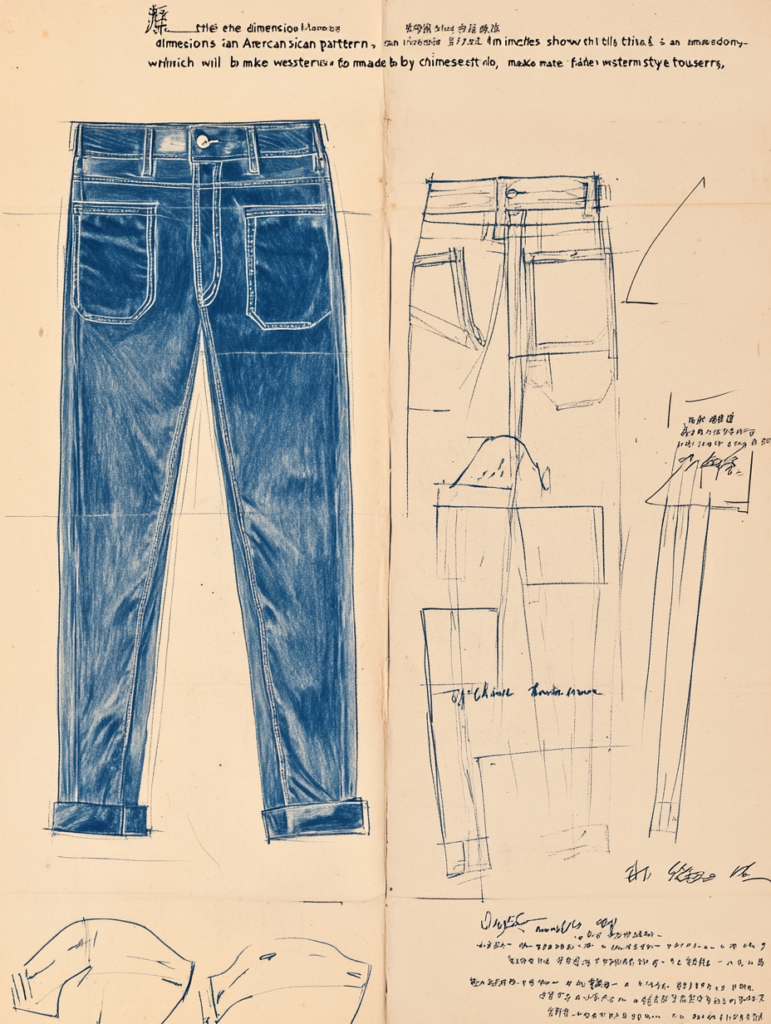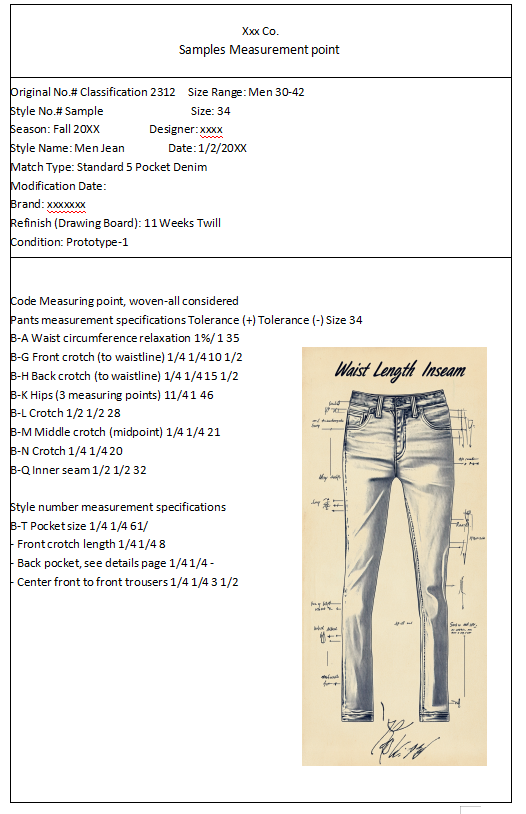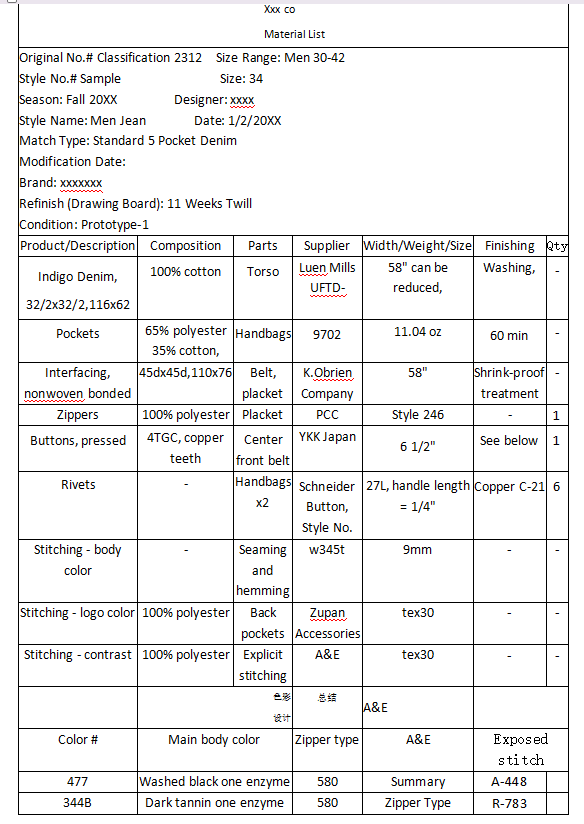
Material List: The Backbone of Garment Production
The Material List section of a process sheet is one of the most essential parts of the garment production process. It provides a detailed breakdown of all the materials needed to create the garment, ensuring that manufacturers know exactly which fabrics, trims, accessories, and other components are required. By specifying the composition, color codes, and suppliers for each material, this section helps ensure the garment is made to the designer’s exact specifications and that the materials meet quality and aesthetic standards.
Purpose of the Material List
The Material List serves several important functions in the garment production process:
- Clarifies material requirements: It ensures that manufacturers understand which fabrics, trims, and accessories are needed, and in what quantities.
- Ensures consistency and quality: By specifying the exact composition, colors, and suppliers, the Material List helps ensure that all materials used are consistent and meet the designer’s standards.
- Prevents mistakes and delays: Clear and detailed material information reduces the risk of errors or delays during production, helping the garment stay on schedule and within budget.
- Facilitates sourcing: It assists the manufacturer in sourcing the right materials from suppliers, ensuring timely delivery of all components needed to create the garment.
Key Elements Included in the Material List
Fabrics
- Fabrics are the core material used to make the majority of the garment. The Material List provides detailed information about the fabric required for the garment’s body, lining, or any other sections that require fabric.
Key information for each fabric:
- Fabric Type: The type of fabric (e.g., cotton, silk, polyester, wool, denim, etc.).
- Composition: The fabric’s fiber content, such as 100% cotton, 70% wool/30% silk, or 85% polyester/15% spandex. This affects the texture, feel, and performance of the fabric.
- Weight: The fabric weight, which can range from light (for summer garments) to heavy (for outerwear). Weight is measured in grams per square meter (gsm) or ounces per yard (oz/yd²).
- Color Code/Swatches: The specific color or pantone number that should be used for the fabric. This ensures that the manufacturer uses the exact shade intended by the designer.
- Supplier: The name and contact information of the supplier who provides the fabric. This helps manufacturers source the material quickly and efficiently.
Example Fabric Description:
- Fabric: Cotton Twill
- Composition: 100% Cotton
- Weight: 250 gsm
- Color: Pantone 19-1557 (Crimson Red)
- Supplier: ABC Fabrics Inc.
A clear description of the fabric ensures that there is no confusion about the type of material required.
Trims
- Trims are the finishing elements that add details and functionality to the garment. They include components such as buttons, zippers, ribbons, labels, and lace.
Key information for each trim:
- Type of Trim: Examples include buttons, zippers, ribbons, lace, elastic bands, and hooks.
- Material: Specify what the trim is made from, such as metal, plastic, leather, or fabric.
- Color: Like fabrics, trims should be assigned specific color codes to match the overall design.
- Size/Dimensions: Some trims, such as buttons or zippers, come in different sizes. The exact measurements should be listed.
- Quantity: The number of trim pieces needed per garment (e.g., 4 buttons, 1 zipper).
- Supplier: The contact details for the supplier of the trim materials.
Example Trim Description:
- Trim: Brass Buttons
- Material: Brass
- Color: Gold
- Size: 20mm diameter
- Quantity: 6 buttons per garment
- Supplier: XYZ Button Co.
The trim section provides clear instructions on the specific components required, making it easier for manufacturers to procure the right elements.
Accessories
- Accessories are additional materials that may be required for specific styles of garments. These could include items like belts, scarves, buckles, chains, or decorative elements such as beads or sequins.
Key information for each accessory:
- Type of Accessory: A description of the accessory (e.g., leather belt, metal buckle, chain, or decorative appliqué).
- Material: Details of the material used for the accessory (e.g., leather, metal, plastic, fabric).
- Size/Dimensions: Specific measurements for accessories like belts, buckles, or decorative embellishments.
- Color: The color code or specific color to match the garment’s overall design.
- Supplier: The name and contact details of the supplier for the accessory.
Example Accessory Description:
- Accessory: Leather Belt
- Material: Genuine Leather
- Color: Black
- Size: 2 inches wide, 36 inches long
- Supplier: Leather Works Ltd.
Accessories often have a significant impact on the garment’s design and functionality, and this section ensures the correct components are included.
Lining and Interfacing
- Lining and interfacing materials are used to provide structure and finishing to garments, especially for jackets, coats, and skirts.
Key information for each lining and interfacing:
- Material: Specify the fabric used for the lining (e.g., satin, polyester, cotton, etc.) or the interfacing (e.g., fusible, non-fusible, woven, or knit).
- Composition: The fiber content (e.g., 100% polyester for lining).
- Weight: The weight of the lining or interfacing (e.g., light, medium, or heavy).
- Color: The color of the lining or interfacing should be specified, especially if it differs from the garment’s main fabric.
- Supplier: Contact information for the supplier providing the lining or interfacing.
Example Lining/Interfacing Description:
- Material: Satin Lining
- Composition: 100% Polyester
- Color: Pantone 11-0602 (Ivory)
- Weight: Light
- Supplier: Satin Fabrics Co.
Lining and interfacing materials are integral to garment construction and need to be specified to maintain the structure, comfort, and finish of the final product.
Special Materials (if applicable)
- For garments that require special materials such as water-resistant fabrics, flame-retardant coatings, or performance textiles (e.g., moisture-wicking fabrics), these should be clearly outlined in the Material List.
Key information for special materials:
- Type of Special Material: For example, Gore-Tex, reflective fabric, or Lycra.
- Properties: Specific characteristics, such as waterproof, stretch, or UV protection.
- Supplier: Name and contact information for the supplier of the special material.
Example Special Material Description:
- Material: Waterproof Fabric
- Composition: 100% Polyester with PU coating
- Properties: Waterproof, breathable
- Supplier: Outdoor Tech Fabrics
Special materials are often critical for performance-oriented garments, such as outerwear or activewear, and need to be described thoroughly.