Process Design in the Fashion Design Process: Turning Concepts into Wearable Products
In the fashion design process, process design plays a crucial role in converting creative ideas into tangible products. It involves various steps, including design analysis, technical drawings, and collaboration with manufacturers, to ensure that the final product meets the designer’s expectations. This process ensures that every aspect of the garment, from its fit to its details, is thoroughly planned before production begins.
In this article, we will explore the steps involved in process design, its importance in the overall fashion development cycle, and how it enhances communication between designers and manufacturers.
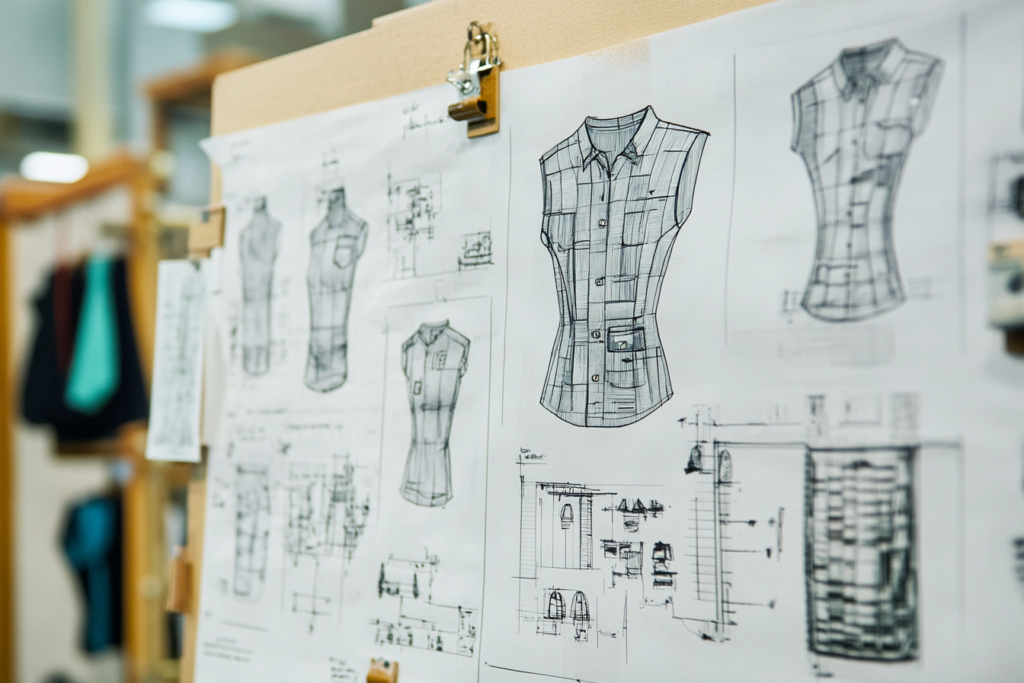

What is Process Design in Fashion?
Process design in fashion is the planning phase where all the technical details of a garment are defined. It includes making accurate technical drawings, deciding on fabric types, evaluating samples, and ensuring that the garment’s fit matches the designer’s vision. Additionally, process design involves thorough communication with factories to guarantee that they understand and execute the designer’s specifications correctly.
| Process Design Step | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Garment Design | Creating accurate style drawings with front and back views, including all design details such as seams and trims. | ✏️ |
| Fabric Calculation | Determining the fabric required based on design specifications, ensuring there’s enough for the garment and its details. | 📐 |
| Sample Evaluation | Assessing the first sample to ensure the fit and design align with expectations. | 👗 |
| Factory Communication | Detailed communication with manufacturers regarding design corrections, fabric use, and garment adjustments. | 🏭 |
| Process Sheet Creation | Creating and sending out a concise process sheet to manufacturers for clarity on product requirements. | 📄 |
The Importance of Process Design in Fashion
Process design is vital for successful fashion production. It bridges the gap between conceptual design and physical garment creation by providing clear and detailed instructions. When designers create a collection, they may face many questions and considerations, such as:
- Seam placement and garment fit: Should the armhole be covered with seams? How many pleats are needed to match a dart?
- Fabric decisions: What is the most cost-effective yet high-quality fabric for the design?
- Practicality and consumer fit: How can high-fashion designs be adapted for the average consumer’s body size and preferences?
- Timely production: How can I meet deadlines with limited time and resources?
These questions are all part of process design, and addressing them helps streamline production, reduce errors, and minimize costly mistakes.
Steps in the Process Design Cycle
The process design cycle involves several key stages to ensure that the design transitions smoothly from concept to production:
1. Creating Accurate Garment Drawings
The first step is to create detailed technical drawings that show the front and back views of the garment, with all design details. These drawings include information on seams, collars, pockets, and any other distinctive features. This step ensures that manufacturers know exactly what to create.
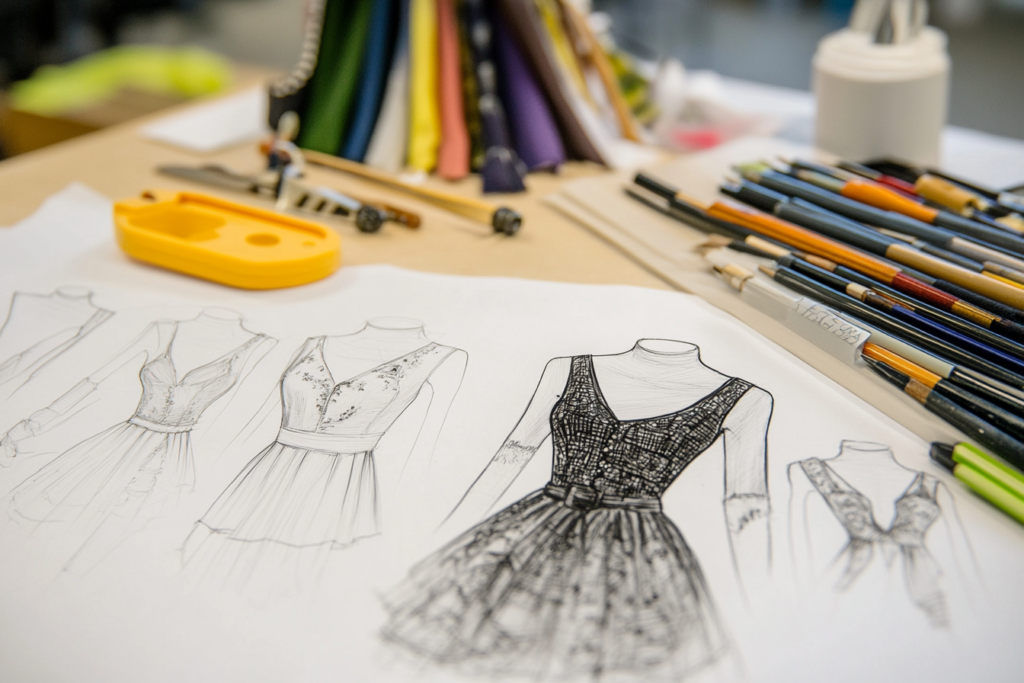

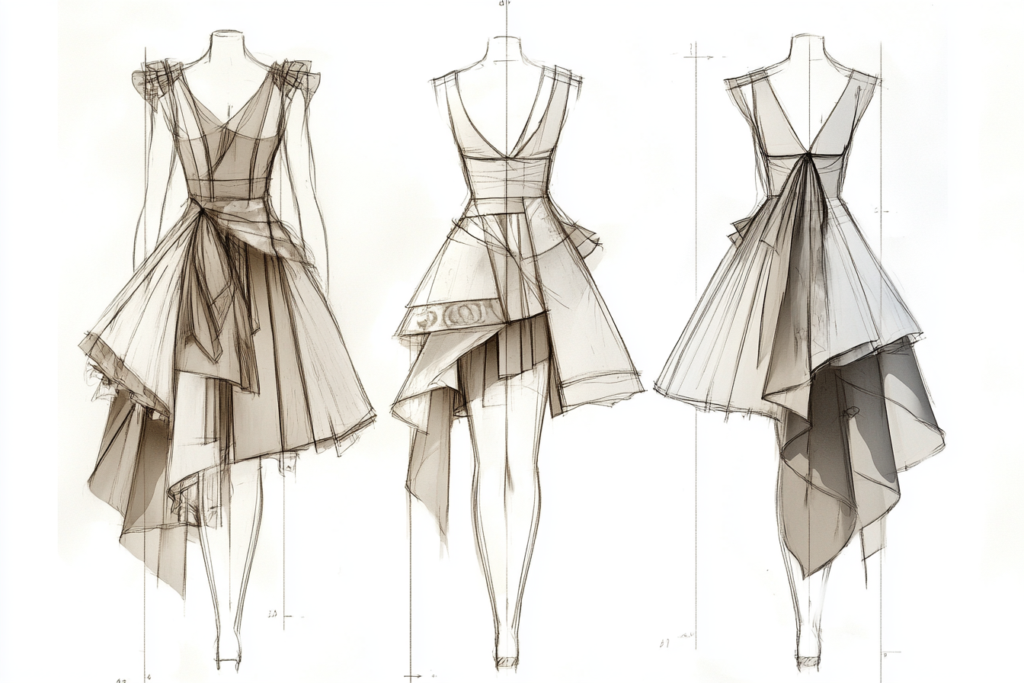
| Garment Design Element | Description | Example | Icon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front View | The front-facing image of the garment, showing key design elements and structure. | Dress front view | 👗 |
| Back View | A reverse view showing back design, closures, and fit. | Jacket back view | 🧥 |
| Design Details | Specific instructions on seams, buttons, zippers, and accessories. | Seam placement | 🧷 |
2. Fabric and Material Calculation
Based on the technical drawings, designers calculate the fabric requirements for each garment. The fabric chosen should match the design’s style, season, and function. Designers ensure the fabric is appropriate for the garment’s fit and structure, considering factors like stretch, weight, and texture.


| Fabric Type | Description | Usage Example | Icon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stretch Fabric | Fabric with elasticity, ideal for form-fitting garments. | Leggings, bodycon dresses | 🧵 |
| Linen | Lightweight and breathable fabric, perfect for warm climates. | Summer blouses, trousers | 🌞 |
| Chiffon | Sheer, delicate fabric often used in evening wear. | Dresses, evening gowns | 🌙 |
3. Sample Evaluation
Once the first sample is made, it undergoes a thorough evaluation to assess the fit and design accuracy. This sample should match the designer’s original vision in terms of proportion, construction, and styling. Fit issues are corrected at this stage, ensuring that the final product is wearable and comfortable.


| Sample Evaluation Point | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Fit | Ensuring the garment fits the target customer’s body type correctly. | 🧍♀️ |
| Design Accuracy | Checking whether all design elements such as seams, fabric choice, and color align with the original concept. | ✅ |
| Functional Testing | Ensuring all elements (e.g., buttons, zippers) work as intended. | 🔧 |
4. Communication with the Factory
Effective communication with the factory is essential to ensure that the design, materials, and specifications are understood. Designers must ensure the factory understands the fit requirements, fabric usage, and other critical aspects. This step can involve sending detailed process sheets, video calls, and on-site visits.


| Communication Aspect | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Process Sheet | A document outlining all the steps and details needed for production, from material sourcing to finishing. | 📄 |
| Correction Feedback | Providing feedback to the manufacturer on sample adjustments, such as fit or fabric change. | ✍️ |
Process Sheets: Ensuring Clarity in Production
The process sheet is a vital document in fashion production. It includes all the technical details of the garment design, such as measurements, fabric types, color swatches, and sewing instructions. Once finalized, the process sheet is sent to the manufacturer, ensuring that they can produce the garment with the required specifications. It serves as the blueprint for creating the first sample and eventually the finished product.


| Process Sheet Components | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Design Sketches | Clear, detailed drawings showing the garment design. | ✏️ |
| Fabric Swatches | Samples of the materials to be used for production. | 🧵 |
| Color References | Specific color codes or fabric swatches used in the collection. | 🎨 |
| Measurement Details | Exact measurements for sizes and proportions for each garment. | 📏 |
The Importance of Process Design in Fashion
Process design is an integral part of the fashion design process that ensures creative ideas are transformed into reality. By carefully creating technical drawings, selecting appropriate fabrics, evaluating samples, and maintaining clear communication with manufacturers, designers can streamline production and ensure that their collections meet both creative and practical requirements.
The use of process sheets, detailed fit evaluations, and consistent collaboration with factories is essential to bringing a fashion collection to market. Efficient process design not only minimizes production errors but also maximizes efficiency, profitability, and consumer satisfaction.